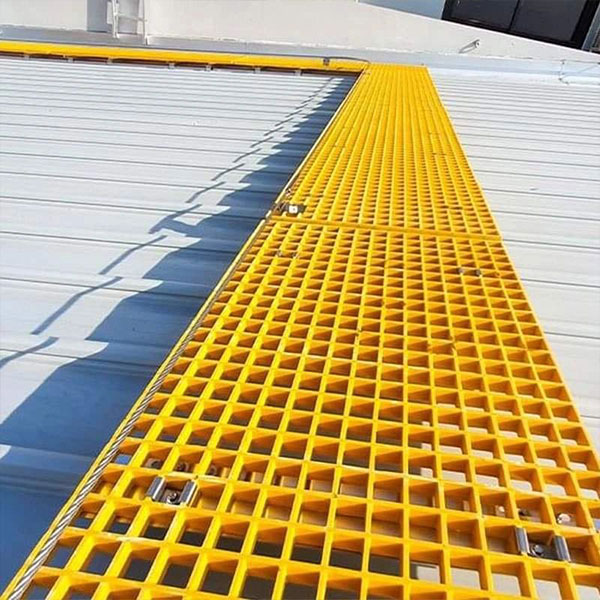
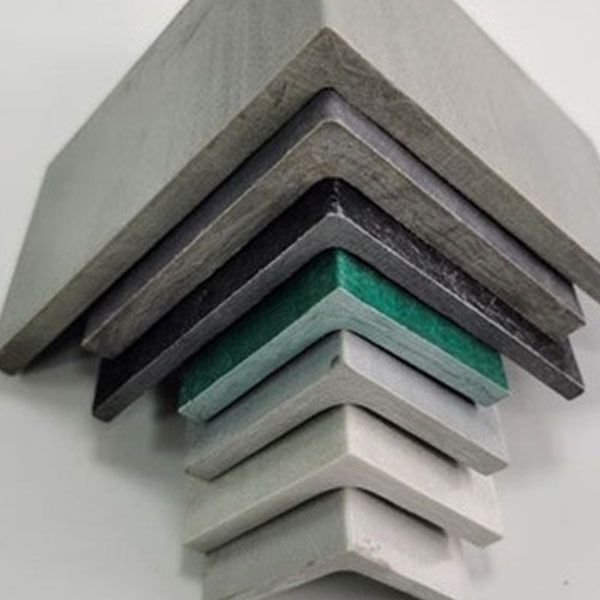
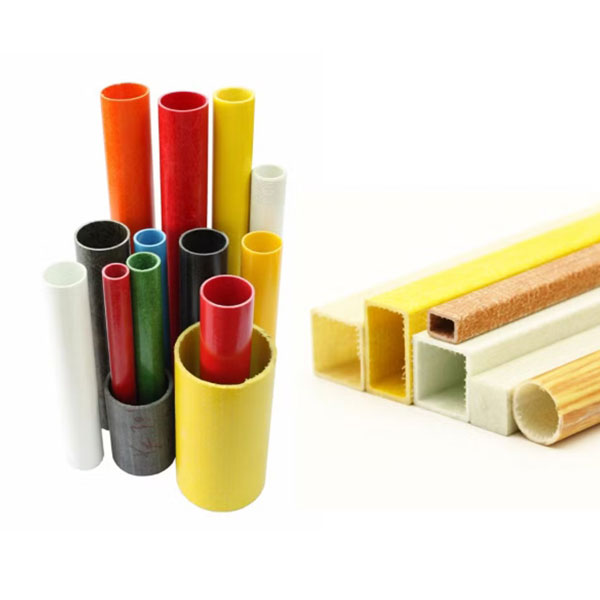
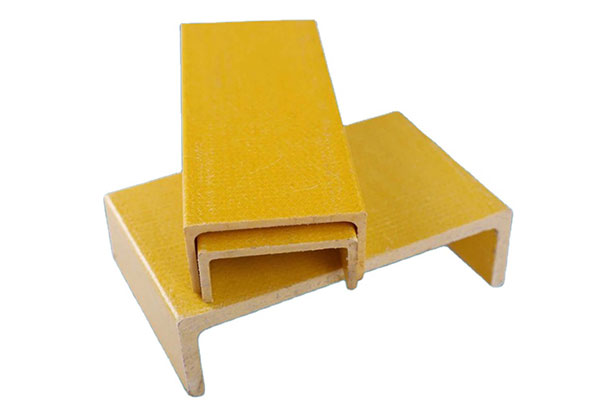
FRP (faserverstärkter Kunststoff) Sondergeformte Teile Sind kundenspezifisch gestaltete Verbundbauteile gemacht, um zu treffen spezifische strukturelle, funktionale oder ästhetische Anforderungen. Im Gegensatz zu Standard-GFK-Profilen werden diese Teile in komplexe Formen und Geometrien Verwendung Formgebungs-, Pultrusions- oder Filamentwickeltechniken.
Einführung zur Produktleistung
Strukturwinkel aus Faserverbundwerkstoffen werden häufig im Bauwesen, in industriellen Anwendungen und bei Infrastrukturprojekten eingesetzt, wo traditionelle Werkstoffe wie Stahl oder Aluminium aufgrund von Korrosion, Gewicht oder Wartungsaufwand nicht geeignet sind.
1. Physikalische Eigenschaften von Faserverbund-Winkelprofilen
Winkelprofile aus Faserverbundwerkstoffen weisen hervorragende mechanische, chemische und thermische Eigenschaften auf und sind daher eine ideale Alternative zu herkömmlichen Metallkonstruktionen.
1.1. Festigkeit und Haltbarkeit
-
Hohes Verhältnis von Festigkeit zu Gewicht: Winkel aus Faserverbundwerkstoffen bieten eine mit Stahl vergleichbare Festigkeit bei gleichzeitig deutlich geringerem Gewicht.
-
Biege- und Zugfestigkeit: Sie weisen eine ausgezeichnete Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Biege- und Zugkräfte auf und gewährleisten so Stabilität und strukturelle Integrität.
-
Schlagfestigkeit: Im Gegensatz zu spröden Materialien kann Faserverbundkunststoff Stöße absorbieren, ohne zu reißen oder sich wesentlich zu verformen.
1.2. Korrosions- und Chemikalienbeständigkeit
-
Beständig gegenüber rauen Umgebungen: Im Gegensatz zu Stahl rostet, korrodiert oder zersetzt sich GFK nicht bei Einwirkung von Feuchtigkeit, Chemikalien oder UV-Strahlung.
-
Chemische Stabilität: Geeignet für Chemieanlagen, Kläranlagen und maritime Anwendungen, bei denen der Kontakt mit korrosiven Substanzen häufig vorkommt.
1.3. Elektrische und thermische Eigenschaften
-
Nicht leitend: FRP-Winkel leiten keinen Strom und sind daher sicher für elektrische Anwendungen und Hochspannungsanwendungen.
-
Wärmedämmung: Im Gegensatz zu Metallen leitet GFK Wärme nicht so leicht, wodurch das Risiko von Verbrennungen und hitzebedingten Problemen verringert wird.
1.4. Feuerbeständigkeit
-
Verfügbare feuerhemmende Optionen: Zur Erfüllung der Brandschutzanforderungen können spezielle Harze wie Phenolharz oder feuerhemmende Polyesterharze verwendet werden.
-
Geringe Rauchentwicklung und geringe Toxizität: Manche GFK-Formulierungen erzeugen im Brandfall nur minimalen Rauch und wenige giftige Dämpfe.
2. Gängige Spezifikationen und Größen
Strukturwinkel aus Faserverbundwerkstoffen sind in verschiedenen Größen, Stärken und Ausführungen erhältlich, um unterschiedlichen Anwendungsbereichen gerecht zu werden.
2.1. Standardabmessungen
-
Beinlängen: Typischerweise liegen sie im Bereich von 25 mm × 25 mm (1” × 1”) Zu 150 mm × 150 mm (6” × 6”)
-
Dicke: Typischerweise 3 mm (1/8") bis 12 mm (1/2")
-
Längen: Standardlängen sind 3 m (10 Fuß), 6 m (20 Fuß) oder individuelle Längen
2.2. Materialzusammensetzung
-
Fasern: E-Glas (am häufigsten verwendet), S-Glas, Kohlenstofffaser (für spezielle Anwendungen)
-
Harze: Polyester, Vinylester (für hohe Korrosionsbeständigkeit), Epoxidharz (für hervorragende mechanische Eigenschaften), Phenolharz (für Feuerbeständigkeit)
2.3. Mechanische Eigenschaften (Ungefähre Werte)
| Eigentum | Typischer Wert |
|---|---|
| Zugfestigkeit | 200-600 MPa |
| Biegefestigkeit | 200-500 MPa |
| Druckfestigkeit | 200-550 MPa |
| Dichte | 1,5–2,0 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul | 20-35 GPa |
3. Vorteile von GFK-Strukturwinkeln
Strukturwinkel aus Faserverbundwerkstoffen bieten zahlreiche Vorteile gegenüber traditionellen Materialien wie Stahl, Aluminium oder Holz.
3.1. Leicht und dennoch robust
-
Bis zu 70% ist leichter als Stahl. bei gleichzeitiger Beibehaltung einer hohen Festigkeit.
-
Leichter zu transportieren, zu handhaben und zu installieren.
3.2. Korrosions- und Witterungsbeständigkeit
-
Ideal für Meeres-, Industrie- und Außenumgebungen wo der Kontakt mit Feuchtigkeit, Salz und Chemikalien üblich ist.
-
Erledigt die Notwendigkeit von Schutzbeschichtungen und Instandhaltung gegen Rost.
3.3. Nichtleitend und nichtmagnetisch
-
Sicher für elektrische Installationen Und MRT-Räume in medizinischen Einrichtungen.
-
Wird verwendet in Kraftwerke, Umspannwerke und Telekommunikationstürme um elektrische Gefahren zu vermeiden.
3.4. Geringer Wartungsaufwand und lange Lebensdauer
-
Im Gegensatz zu Stahl benötigt GFK keine Lackieren, Verzinken oder Beschichten um die Haltbarkeit zu gewährleisten.
-
Resistent gegen biologischen Abbau wie z.B. Fäulnis, Schimmel und Insektenschäden.
-
Lange Lebensdauer von 20-50 Jahre abhängig von der Anwendung und der Umgebung.
3.5. Einfache Fertigung und Installation
-
Kann sein zugeschnitten, gebohrt und montiert unter Verwendung gängiger Werkzeuge.
-
Kein Schweißen erforderlich, wodurch die Installation sicherer und einfacher wird.
-
Sonderformen und -größen können nach Bedarf gefertigt werden.
4. Nachteile von FRP-Strukturwinkeln
Trotz seiner vielen Vorteile weist der GFK-Strukturwinkel einige Einschränkungen auf:
4.1. Höhere Anfangskosten
-
Teurer im Vergleich zu traditionellen Werkstoffen wie Stahl oder Aluminium, bezogen auf die Stückzahl.
-
Jedoch niedrigere Wartungskosten Und lange Lebensdauer können die anfängliche Investition ausgleichen.
4.2. Geringere Steifigkeit im Vergleich zu Stahl
-
Größere Durchbiegung unter Last, was in einigen Anwendungsfällen eine zusätzliche Verstärkung erfordert.
-
Nicht immer geeignet für hochbelastbare Strukturen es sei denn, es ist ordnungsgemäß konstruiert.
4.3. UV-Abbau
-
Längere Exposition gegenüber direktes Sonnenlicht kann zu Oberflächenbeeinträchtigungen und Farbverblassung führen.
-
Erfordert UV-beständige Beschichtungen für den langfristigen Einsatz im Freien.
4.4. Eingeschränkte Hochtemperaturleistung
-
Standard-FRP-Dose Weichen bei Temperaturen über 150-200°C auf.
-
Für brandgefährdete Umgebungen werden spezielle Hochtemperaturharze (wie z. B. Phenolharze) benötigt.
4.5. Schwer zu recyceln
-
Faserverbundwerkstoffe sind nicht leicht recycelbar im Vergleich zu Stahl oder Aluminium.
-
Die Entsorgungsmöglichkeiten sind begrenzt, obwohl sich einige Unternehmen auf das Recycling von Verbundwerkstoffen spezialisiert haben.
5. Anwendungen von FRP-Strukturwinkeln
Aufgrund ihrer hervorragenden Eigenschaften finden GFK-Winkelprofile in verschiedenen Branchen breite Anwendung.
5.1. Industrielle Anwendungen
-
Chemische Verarbeitungsanlagen: Halterungen und Rahmen für Geräte, die korrosiven Chemikalien ausgesetzt sind.
-
Wasser- und Abwasseraufbereitung: Strukturelle Stützen, Laufstege und Plattformen, die beständig gegen Feuchtigkeit und Chemikalien sind.
5.2. Marine & Offshore
-
Dock- und Pierbau: Beständig gegen Salzwasser und korrodiert nicht wie Stahl.
-
Schiffbau: Wird in nichttragenden Bauteilen verwendet, die leichte, korrosionsbeständige Werkstoffe erfordern.
5.3. Infrastruktur und Bauwesen
-
Brücken und Gehwege: Wird für Fußgängerbrücken und Zugangsbauwerke in korrosiven Umgebungen verwendet.
-
Anwendungen im Eisenbahn- und Straßenbereich: Nichtleitende Strukturen für Eisenbahnsignalanlagen und Umspannwerke.
5.4. Elektrotechnik und Telekommunikation
-
Stromverteilung: Wird in Hochspannungsumgebungen eingesetzt, in denen Metallkonstruktionen eine Gefahr darstellen würden.
-
Telekommunikationstürme: Träger und Rahmen für Antennenstrukturen und Kommunikationspanels.
6. Schlussfolgerung
FRP-Strukturwinkel bieten eine eine hervorragende Alternative zu Stahl, Aluminium und Holz in Anwendungen, die Korrosionsbeständigkeit, geringes Gewicht, Festigkeit und elektrische Isolation. Ihre lange Lebensdauer, geringer Wartungsaufwand und einfache Fertigung dadurch ideal für Industrie-, Schiffs-, Infrastruktur- und Elektroanwendungen.
Jedoch, höhere Anschaffungskosten, geringere Steifigkeit und begrenzte Recyclingmöglichkeiten Bei der Wahl von Faserverbundwerkstoffen gegenüber herkömmlichen Materialien sollten Aspekte berücksichtigt werden. Eine sachgemäße Konstruktion und Materialauswahl können den Nutzen maximieren von FRP-Strukturwinkeln, was sie zu einer wertvollen Lösung macht für herausfordernde Umgebungen.
FRP-Strukturwinkel
Serie :
Hauptprodukte >Anwendung
Industrieanwendungen, Schifffahrt & Offshore, Infrastruktur & Bauwesen, Elektrotechnik & Telekommunikation
Markenname :
TF-Verbundwerkstoff
Produktname :
FRP-Strukturwinkel
Material :
Glasfaser
Farbe :
Grau, Sonstige
FAQ
Q :
Wie lange ist die Lebensdauer von GFK-Sonderformen?
A :
GFK-Sonderformen haben eine Lebensdauer von über 25 Jahren und übertreffen damit viele traditionelle Werkstoffe wie Holz (5-10 Jahre) oder Stahl (10-15 Jahre, je nach Bedingungen) deutlich.
Q :
Können GFK-Sonderformen im Freien verwendet werden?
A :
Ja! GFK-Sonderformen sind äußerst UV-beständig und witterungsbeständig und eignen sich daher ideal für den Außeneinsatz in rauen Umgebungen wie in der Schifffahrt, in Chemieanlagen und im Infrastrukturbereich.
Q :
Welche typischen Abmessungen und Größen haben GFK-Sonderformen?
A :
Die Abmessungen von GFK-Sonderformen variieren je nach Anwendung und Konstruktion erheblich. Gängige Größen sind jedoch: Länge: Kann an die Projektanforderungen angepasst werden (üblicherweise 3 m bis 6 m). Dicke: Typischerweise 3 mm bis 50 mm oder mehr, abhängig von den Festigkeitsanforderungen. Breite: Kann an die gewünschte Form und Funktion angepasst werden (von kleinen Profilen bis hin zu großen Platten). Kundenspezifische Formen wie gebogene, abgewinkelte und hohle Profile können exakt nach Konstruktionsvorgaben gefertigt werden.
Andere verwandte Produkte