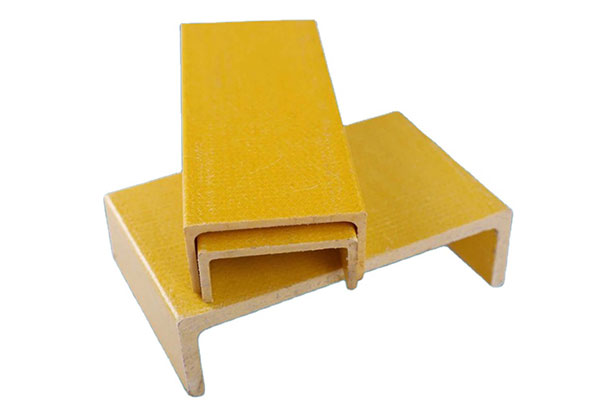
FRP (plastica rinforzata con fibre) Parti di forma speciale Sono componenti compositi progettati su misura fatto per incontrare requisiti strutturali, funzionali o estetici specifici. A differenza dei profili FRP standard, queste parti sono prodotte in forme e geometrie complesse usando tecniche di stampaggio, pultrusione o avvolgimento di filamenti.
Introduzione alle prestazioni del prodotto
Gli angolari strutturali in FRP sono comunemente utilizzati nell'edilizia, nelle applicazioni industriali e nei progetti infrastrutturali in cui i materiali tradizionali come l'acciaio o l'alluminio potrebbero non essere adatti a causa di problemi di corrosione, peso o manutenzione.
1. Proprietà fisiche dell'angolo strutturale FRP
Gli angolari strutturali in FRP presentano eccellenti proprietà meccaniche, chimiche e termiche, il che li rende un'alternativa ideale alle tradizionali strutture metalliche.
1.1. Resistenza e durata
-
Elevato rapporto resistenza/peso: Gli angoli in FRP offrono una resistenza paragonabile a quella dell'acciaio, pur essendo notevolmente più leggeri.
-
Resistenza alla flessione e alla trazione: Presentano un'eccellente resistenza alle forze di flessione e trazione, garantendo stabilità e integrità strutturale.
-
Resistenza all'impatto: A differenza dei materiali fragili, l'FRP è in grado di assorbire gli urti senza screpolarsi o deformarsi in modo significativo.
1.2. Resistenza alla corrosione e agli agenti chimici
-
Resistente agli ambienti difficili: A differenza dell'acciaio, la FRP non arrugginisce, non si corrode e non si degrada se esposta a umidità, sostanze chimiche o radiazioni UV.
-
Stabilità chimica: Adatto per impianti chimici, impianti di trattamento delle acque reflue e applicazioni marine in cui è frequente l'esposizione a sostanze corrosive.
1.3. Proprietà elettriche e termiche
-
Non conduttore: Gli angoli in FRP non conducono elettricità, il che li rende sicuri per applicazioni elettriche e ad alta tensione.
-
Isolamento termico: A differenza dei metalli, la FRP non trasferisce facilmente il calore, riducendo il rischio di ustioni e problemi legati al calore.
1.4. Resistenza al fuoco
-
Opzioni ignifughe disponibili: Per soddisfare i requisiti di sicurezza antincendio è possibile utilizzare resine speciali come il poliestere fenolico o ignifugo.
-
Basso fumo e tossicità: Alcune formulazioni FRP producono una quantità minima di fumo e vapori tossici in caso di incendio.
2. Specifiche e dimensioni comuni
Gli angolari strutturali in FRP sono disponibili in varie dimensioni, spessori e configurazioni per adattarsi a diverse applicazioni.
2.1. Dimensioni standard
-
Lunghezze delle gambe: In genere vanno da 25 mm × 25 mm (1" × 1") A 150 mm × 150 mm (6" × 6")
-
Spessore: Tipicamente da 3 mm (1/8") a 12 mm (1/2")
-
Lunghezze: Le lunghezze standard sono 3 m (10 piedi), 6 m (20 piedi) o lunghezze personalizzate
2.2. Composizione del materiale
-
Fibre: Vetro E (il più comune), vetro S, fibra di carbonio (per applicazioni specializzate)
-
Resine: Poliestere, vinilestere (per elevata resistenza alla corrosione), epossidico (per proprietà meccaniche superiori), fenolico (per resistenza al fuoco)
2.3. Proprietà meccaniche (Valori approssimativi)
| Proprietà | Valore tipico |
|---|---|
| Resistenza alla trazione | 200-600 MPa |
| Resistenza alla flessione | 200-500 MPa |
| Resistenza alla compressione | 200-550 MPa |
| Densità | 1,5-2,0 g/cm³ |
| Modulo di elasticità | 20-35 GPa |
3. Vantaggi dell'angolo strutturale FRP
Gli angolari strutturali in FRP offrono numerosi vantaggi rispetto ai materiali tradizionali come acciaio, alluminio o legno.
3.1. Leggero ma resistente
-
Fino a 70% più leggero dell'acciaio mantenendo un'elevata resistenza.
-
Più facile da trasportare, maneggiare e installare.
3.2. Resistenza alla corrosione e agli agenti atmosferici
-
Ideale per ambienti marini, industriali ed esterni dove l'esposizione all'umidità, al sale e alle sostanze chimiche è comune.
-
Elimina la necessità di rivestimenti protettivi e manutenzione contro la ruggine.
3.3. Non conduttivo e non magnetico
-
Sicuro per installazioni elettriche E Sale per risonanza magnetica nelle strutture mediche.
-
Utilizzato in centrali elettriche, sottostazioni e torri per telecomunicazioni per prevenire rischi elettrici.
3.4. Bassa manutenzione e lunga durata
-
A differenza dell'acciaio, l'FRP non richiede verniciatura, zincatura o rivestimento per mantenere la durevolezza.
-
Resistente alla degradazione biologica come marciume, muffa e danni causati dagli insetti.
-
Lunga durata di vita di 20-50 anni a seconda dell'applicazione e dell'ambiente.
3.5. Facilità di fabbricazione e installazione
-
Può essere tagliato, forato e assemblato utilizzando strumenti standard.
-
Non è richiesta alcuna saldatura, rendendo l'installazione più sicura e semplice.
-
È possibile realizzare forme e dimensioni personalizzate in base alle esigenze.
4. Svantaggi dell'angolo strutturale FRP
Nonostante i suoi numerosi vantaggi, l'angolare strutturale in FRP presenta alcune limitazioni:
4.1. Costo iniziale più elevato
-
Più costoso rispetto ai materiali tradizionali come acciaio o alluminio su base unitaria.
-
Tuttavia, il minori costi di manutenzione E lunga durata di vita può compensare l'investimento iniziale.
4.2. Rigidità inferiore rispetto all'acciaio
-
Maggiore flessione sotto carico, che in alcune applicazioni richiede un rinforzo aggiuntivo.
-
Non sempre adatto per strutture portanti ad alto carico se non adeguatamente progettati.
4.3. Degradazione UV
-
Esposizione prolungata a luce solare diretta può causare il degrado della superficie e lo sbiadimento del colore.
-
Richiede Rivestimenti resistenti ai raggi UV per uso esterno a lungo termine.
4.4. Prestazioni limitate alle alte temperature
-
La FRP standard può ammorbidire a temperature superiori a 150-200°C.
-
Per gli ambienti soggetti a incendi sono necessarie resine speciali per alte temperature (come quelle fenoliche).
4.5. Difficile da riciclare
-
I materiali FRP sono non facilmente riciclabile rispetto all'acciaio o all'alluminio.
-
Le possibilità di smaltimento sono limitate, anche se alcune aziende sono specializzate nel riciclaggio di materiali compositi.
5. Applicazioni dell'angolo strutturale FRP
Grazie alle loro eccellenti proprietà, gli angolari strutturali in FRP sono ampiamente utilizzati in vari settori industriali.
5.1. Applicazioni industriali
-
Impianti di lavorazione chimica: Supporti e intelaiature per apparecchiature esposte a sostanze chimiche corrosive.
-
Trattamento delle acque e delle acque reflue: Supporti strutturali, passerelle e piattaforme resistenti all'umidità e agli agenti chimici.
5.2. Marina e offshore
-
Costruzione di banchine e moli: Resistente all'acqua salata e non si corrode come l'acciaio.
-
Costruzione navale: Utilizzato in componenti non strutturali che richiedono materiali leggeri e resistenti alla corrosione.
5.3. Infrastrutture e costruzioni
-
Ponti e passerelle: Utilizzato in ponti pedonali e strutture di accesso in ambienti corrosivi.
-
Applicazioni ferroviarie e stradali: Strutture non conduttive per supporti di segnali ferroviari e sottostazioni elettriche.
5.4. Elettricità e telecomunicazioni
-
Distribuzione di energia: Utilizzato in ambienti ad alta tensione in cui le strutture metalliche potrebbero creare pericoli.
-
Torri per telecomunicazioni: Supporti e telai per strutture di antenne e pannelli di comunicazione.
6. Conclusion
Gli angoli strutturali FRP offrono un ottima alternativa all'acciaio, all'alluminio e al legno nelle applicazioni che richiedono resistenza alla corrosione, resistenza alla leggerezza e isolamento elettrico. Loro lunga durata, bassa manutenzione e facilità di fabbricazione li rendono ideali per applicazioni industriali, marine, infrastrutturali ed elettriche.
Tuttavia, costi iniziali più elevati, minore rigidità e opzioni di riciclaggio limitate dovrebbero essere considerati quando si sceglie FRP rispetto ai materiali tradizionali. Una progettazione e una selezione dei materiali adeguate possono massimizzare i benefici di angolari strutturali in FRP, rendendoli una soluzione preziosa per ambienti difficili.
Angolo strutturale FRP
Serie:
Prodotti principali >applicazione
Applicazioni industriali, nautica e offshore, infrastrutture e costruzioni, elettricità e telecomunicazioni
Marchio :
TFcomposito
Nome del prodotto :
Angolo strutturale FRP
Materiale :
Fibra di vetro
Colore :
Grigio,Altro
FAQ
Q :
Quanto durano i componenti FRP di forma speciale?
UN :
Le parti in FRP di forma speciale hanno una durata di oltre 25 anni, superando di gran lunga quella di molti materiali tradizionali come il legno (5-10 anni) o l'acciaio (10-15 anni, a seconda delle condizioni).
Q :
I componenti FRP di forma speciale possono essere utilizzati all'esterno?
UN :
Sì! I componenti FRP di forma speciale sono altamente resistenti ai raggi UV e alle intemperie, il che li rende ideali per l'uso all'aperto in ambienti difficili come applicazioni marine, impianti chimici e infrastrutture.
Q :
Quali sono le dimensioni e le misure tipiche delle parti speciali in FRP?
UN :
Le dimensioni dei componenti in FRP di forma speciale variano notevolmente a seconda dell'applicazione e del design. Tuttavia, le dimensioni più comuni includono: Lunghezza: può essere personalizzata in base ai requisiti del progetto (comunemente da 3 m a 6 m). Spessore: in genere da 3 mm a 50 mm o più a seconda delle esigenze di resistenza. Larghezza: può essere personalizzata in base alla forma e alla funzione richieste (dai piccoli profili alle grandi lastre). È possibile creare forme personalizzate come profili curvi, angolati e cavi per soddisfare le specifiche di progettazione.
Altri prodotti correlati