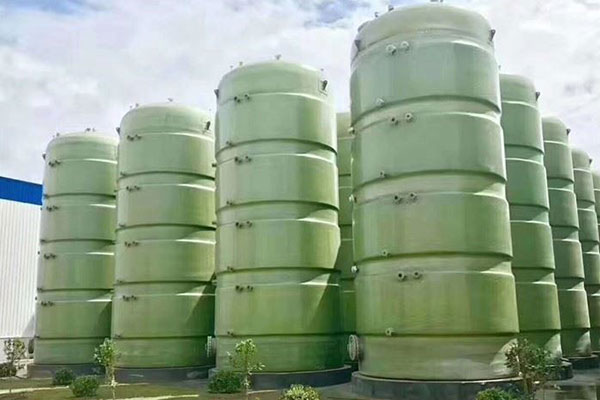
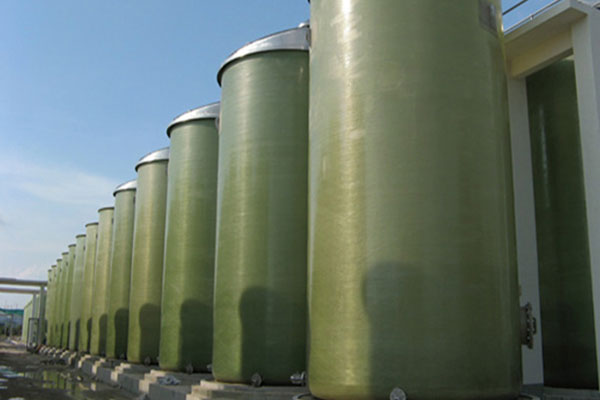
FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) fermentation tanks are corrosion-resistant, lightweight, and highly durable vessels designed for microbial fermentation processes in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, agriculture, chemical processing, and biofuel production. These tanks are engineered using advanced composite technology, combining a chemical-resistant inner lining with high-strength fiberglass reinforcement to create a sanitary, thermally stable, and long-lasting vessel capable of withstanding both biological and chemical agents.
Introducción al rendimiento del producto
As the demand for cost-effective, long-life fermentation vessels increases, FRP fermentation tanks have become a preferred alternative to traditional stainless steel and carbon steel tanks, especially where chemical or pH exposure is a concern.
Características clave
-
Chemical & Corrosion Resistance: Excellent resistance to organic acids, bases, solvents, and disinfectants used in cleaning (CIP/SIP systems).
-
Estabilidad térmica: Maintains mechanical integrity under fermentation temperatures up to 120°C depending on resin system.
-
Sanitary Inner Surface: Smooth, non-porous, food-safe inner liner prevents contamination, easy to clean and sterilize.
-
Customizable Configurations: Built in vertical or horizontal form, with options for conical bottoms, heating/cooling jackets, agitators, and nozzles.
-
Ligero y de alta resistencia: Easy transportation and installation, especially for large-scale tanks.
-
Económico: Lower lifecycle cost compared to metal fermentation tanks due to corrosion resistance and minimal maintenance.
Aplicaciones
FRP fermentation tanks are suitable for aerobic and anaerobic fermentation processes in:
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Antibiotics, insulin, enzymes, and probiotics.
-
Food & Beverage Industry: Yogurt, kombucha, vinegar, beer, wine, soy sauce, pickles, and kimchi.
-
Agricultura: Animal feed fermentation, silage, and biofertilizer production.
-
Biotechnology: Bioethanol, biogas, bioplastics, algae, and microbial biomass production.
-
Tratamiento de aguas residuales: Anaerobic digestion for methane production.
-
Distilleries: Alcohol and spirit fermentation using molasses, grains, or fruits.
Construction & Materials
FRP fermentation tanks are fabricated through either bobinado de filamento, bandeja manual, o infusión al vacío, using corrosion-resistant thermosetting resins and high-strength fiberglass.
1. Inner Liner (Corrosion Barrier)
| Liner Type | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Resina de éster de vinilo | Used for high chemical and thermal resistance; suitable for aggressive fermentation substrates. |
| Resina de poliéster isoftálico | Cost-effective, general-purpose food-safe applications. |
| FDA-Approved Resin | Food-grade certified liners for direct contact with consumables. |
| Antimicrobial Coating (Optional) | Prevents microbial growth on the surface, reducing contamination risk. |
2. Structural Layer
-
Reinforced with fieltro de vidrio, woven roving, o filament-wound continuous fibers.
-
Optimized laminate schedule for hoop and axial strength, especially for tall vertical tanks.
3. External Finish
-
Gelcoat Layer: UV-resistant coating for outdoor exposure.
-
Opciones de color: Grey, white, green, blue, or custom colors.
-
Aislamiento térmico: Optional PU foam or rockwool jacketing for temperature-sensitive fermentation.
Design Configurations
| Parámetro | Options |
|---|---|
| Forma | Vertical cylindrical, horizontal, conical bottom, flat bottom |
| Volume Range | 500 L – 300,000+ L |
| Tank Mounting | Skirt support, leg support, saddle-mounted (horizontal) |
| Agitation | Top-entry or side-entry agitators for aerobic mixing |
| Jacketed Systems | External coil or full-wall jacket for heating/cooling |
| Manway Access | Top manhole, side manhole, sanitary clamps |
| Instrumentation | pH sensor ports, temperature probes, sight glasses, CIP nozzles |
| Accesorios | Breather valves, vent filters, level indicators, overflow outlets |
Sanitation & Sterility
-
Smooth inner surface with resin-rich liner prevents microbial buildup.
-
CIP/SIP Ready: Compatible with steam-in-place and clean-in-place systems.
-
Antimicrobial liners optional for high-purity applications.
Thermal Performance
-
Operating temperature range: -40°C to 120°C (resin-dependent)
-
Insulated versions maintain fermentation temperatures with minimal energy loss.
-
Optional thermal jackets (glycol or steam) support temperature control.
Ficha técnica (TDS)
Propiedades mecánicas
| Propiedad | Valor típico | Estándar de prueba |
|---|---|---|
| Resistencia a la tracción | 120–200 MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Resistencia a la flexión | 180–300 MPa | ASTM D790 |
| Resistencia a la compresión | 150–250 MPa | ASTM D695 |
| Módulo de elasticidad | 7.000–12.000 MPa | ASTM D790 |
| Resistencia al impacto | >100 J/m | ASTM D256 |
| Dureza Barcol | 40–50 | ASTM D2583 |
Propiedades térmicas
| Propiedad | Valor |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Temperature (Vinyl Ester) | 110–120°C |
| Max Operating Temperature (Polyester) | 65–70°C |
| Conductividad térmica | 0.3–0.5 W/mK |
| Coeficiente de expansión térmica | 2,5 × 10⁻⁵ /°C |
Chemical Resistance (Common Substances in Fermentation)
| Chemical/Substance | Clasificación de resistencia |
|---|---|
| Lactic Acid | Excelente |
| Ethanol (95%) | Excelente |
| Acetic Acid | Excelente |
| Citric Acid | Excelente |
| Yeast Extract | Excelente |
| Sodium Hydroxide (2–5%) | Excelente |
| Hydrogen Peroxide (3%) | Bien |
| Amoníaco | Bien |
| Phosphoric Acid | Bien |
| Cleaning Detergents | Excelente |
Sanitation Properties
-
Inner surface finish: ≤ 0.5 μm (sanitary polish)
-
FDA/USDA compliance available
-
CIP/SIP tested (steam up to 121°C for 30 minutes)
Standards & Certifications
-
ASME RTP-1: For reinforced thermoset plastic vessels
-
ASTM D3299 / D4097: Filament-wound and contact-molded tanks
-
Norma ISO 9001:2015: Quality management compliance
-
NSF/ANSI 61: Drinking water and food-grade compliance (optional)
-
FDA 21 CFR 177.2420: Food contact resin compliance
Advantages of FRP Over Stainless Steel Tanks
| Característica | FRP Tank | Tanque de acero inoxidable |
|---|---|---|
| Resistencia a la corrosión | Excelente | Prone to corrosion with acids/alkalis |
| Peso | Ligero | Pesado |
| Costo | Más bajo | High initial & maintenance cost |
| Personalización | Alto | Medio |
| Aislamiento térmico | Built-in options | External insulation required |
| Mantenimiento | Mínimo | Frequent cleaning required |
| Lead Time | Shorter | Longer |
Instrucciones de instalación
-
Base: Concrete slab or steel platform with level surface
-
Hoisting: Use built-in lifting lugs or straps; avoid side pressure
-
Anchoring: For outdoor or seismic zones, anchor to resist uplift
-
Conexiones: Flexible couplings recommended to allow for thermal expansion
-
Pruebas: Hydrostatic leak testing prior to commissioning
Consejos de mantenimiento
-
Inspect tank internals annually for wear or damage
-
Sanitize before and after each fermentation cycle
-
Use non-abrasive CIP solutions
-
Check gaskets, seals, and nozzles for cracks or buildup
Optional Upgrades
-
Stainless steel or HDPE nozzles
-
Anti-foam spray rings
-
External viewing windows
-
Agitator with VFD controller
-
PLC control system for real-time fermentation monitoring
-
Flame arrestors for alcohol fermentation
Customization Capabilities
We offer full customization:
-
Volume: 0.5 m³ – 300 m³
-
Geometry: Cylindrical, rectangular, squat-type
-
Port arrangements: Top, bottom, side
-
Heating/cooling: Coils, jackets, electric pads
-
Certifications: CE, ISO, NSF, FDA, ATEX (on request)
Tanques de fermentación de FRP (plástico reforzado con fibra de vidrio)
Serie :
Productos proxy >solicitud
Industria farmacéutica: Antibióticos, insulina, enzimas y probióticos. Industria alimentaria y de bebidas: Yogur, kombucha, vinagre, cerveza, vino, salsa de soja, encurtidos y kimchi. Agricultura: Fermentación de piensos, ensilado y producción de biofertilizantes. Biotecnología: Producción de bioetanol, biogás, bioplásticos, algas y biomasa microbiana. Tratamiento de aguas residuales: Digestión anaeróbica para la producción de metano. Destilerías: Fermentación de alcoholes y bebidas espirituosas con melaza, cereales o frutas.
Material :
PRFV
Tipo :
Tanques de fermentación de FRP (plástico reforzado con fibra de vidrio)
Preguntas más frecuentes
P:
What are the advantages of using FRP tanks for fermentation?
A :
Excellent corrosion and chemical resistance Lower cost than stainless steel tanks Lightweight and easier to transport/install Long service life (15–30 years) Customizable shapes, volumes, and connections Compatible with CIP/SIP systems for sanitation
P:
Are FRP tanks food-grade and safe for consumables?
A :
Yes. When manufactured with FDA-approved resins or NSF 61-certified linings, FRP fermentation tanks are 100% food-safe and suitable for direct contact with food or beverages like yogurt, beer, wine, soy sauce, and vinegar.
P:
What resin is best for fermentation tanks?
A :
Vinyl Ester Resin: For strong chemical resistance (e.g. acidic fermentation) Isophthalic Polyester Resin: For general food applications Bisphenol A (Epoxy-based): For high-temperature resistance FDA and antimicrobial-grade resin options are available
P:
What volumes are available?
A :
Small-scale: 500 L – 5,000 L Medium-scale: 10,000 L – 50,000 L Large-scale: 100,000 L – 300,000+ L All volumes can be customized according to your process needs.
P:
Can FRP fermentation tanks be used outdoors?
A :
Yes. FRP tanks can be designed with UV-resistant gelcoats and weatherproof exteriors for long-term outdoor use. Optional insulation and thermal jackets are available to stabilize temperature in fluctuating environments.
P:
What temperature ranges can FRP tanks withstand?
A :
Standard FRP tanks: up to 70°C (polyester) High-performance tanks (vinyl ester): up to 120°C Optional: thermal insulation and glycol/stainless steel jacketed systems
P:
How do I clean or sterilize an FRP fermentation tank?
A :
FRP tanks support CIP (Clean-in-Place) and SIP (Steam-in-Place) processes: Use mild alkaline/acidic solutions and warm water Max steam temperature: 121°C for 30 minutes (with high-temp resin) Smooth internal surface prevents bacterial buildup
Otros productos relacionados