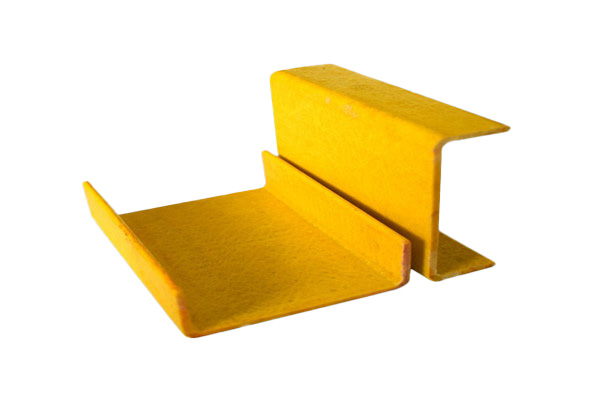
PRV (Plastique Renforcé de Fibres) Pièces de forme spéciale sont composants composites conçus sur mesure conçu pour répondre exigences structurelles, fonctionnelles ou esthétiques spécifiques. Contrairement aux profilés FRP standard, ces pièces sont fabriquées en formes et géométries complexes en utilisant techniques de moulage, de pultrusion ou d'enroulement filamentaire.
Présentation des performances du produit
Les cornières structurelles en PRV sont couramment utilisées dans la construction, les applications industrielles et les projets d'infrastructure où les matériaux traditionnels comme l'acier ou l'aluminium peuvent ne pas convenir en raison de problèmes de corrosion, de poids ou d'entretien.
1. Propriétés physiques des cornières structurelles en PRF
Les cornières structurelles en PRF présentent d'excellentes propriétés mécaniques, chimiques et thermiques, ce qui en fait une alternative idéale aux structures métalliques traditionnelles.
1.1. Résistance et durabilité
-
Rapport résistance/poids élevé : Les cornières en PRV offrent une résistance comparable à celle de l'acier tout en étant nettement plus légères.
-
Résistance à la flexion et à la traction : Elles présentent une excellente résistance à la flexion et à la traction, assurant ainsi stabilité et intégrité structurelle.
-
Résistance aux chocs : Contrairement aux matériaux fragiles, les PRF peuvent absorber les chocs sans se fissurer ni se déformer de manière significative.
1.2. Résistance à la corrosion et aux produits chimiques
-
Résistant aux environnements difficiles : Contrairement à l'acier, le PRV ne rouille pas, ne se corrode pas et ne se dégrade pas lorsqu'il est exposé à l'humidité, aux produits chimiques ou aux rayons UV.
-
Stabilité chimique : Convient aux usines chimiques, aux stations d'épuration des eaux usées et aux applications marines où l'exposition à des substances corrosives est fréquente.
1.3. Propriétés électriques et thermiques
-
Non conductrice: Les cornières en PRV ne conduisent pas l'électricité, ce qui les rend sûres pour les applications électriques et à haute tension.
-
Isolation thermique : Contrairement aux métaux, le PRV ne transmet pas facilement la chaleur, réduisant ainsi le risque de brûlures et de problèmes liés à la chaleur.
1.4. Résistance au feu
-
Options ignifuges disponibles : Des résines spéciales telles que les résines phénoliques ou le polyester ignifugé peuvent être utilisées pour répondre aux exigences en matière de sécurité incendie.
-
Faible dégagement de fumée et faible toxicité : Certaines formulations de PRV produisent un minimum de fumée et de vapeurs toxiques en cas d'incendie.
2. Spécifications et dimensions courantes
Les cornières structurelles en PRV sont disponibles en différentes tailles, épaisseurs et configurations pour s'adapter à différentes applications.
2.1. Dimensions standard
-
Longueur des jambes : Généralement, cela va de 25 mm × 25 mm (1 po × 1 po) à 150 mm × 150 mm (6” × 6”)
-
Épaisseur: Typiquement 3 mm (1/8 po) à 12 mm (1/2 po)
-
Longueurs : Les longueurs standard sont 3 m (10 pi), 6 m (20 pi) ou longueurs personnalisées
2.2. Composition du matériau
-
Fibres : Fibre de verre E (la plus courante), fibre de verre S, fibre de carbone (pour des applications spécialisées)
-
Résines : Polyester, vinylester (pour une haute résistance à la corrosion), époxy (pour des propriétés mécaniques supérieures), phénolique (pour la résistance au feu)
2.3. Propriétés mécaniques (Valeurs approximatives)
| Propriété | Valeur typique |
|---|---|
| Résistance à la traction | 200-600 MPa |
| Résistance à la flexion | 200-500 MPa |
| Résistance à la compression | 200-550 MPa |
| Densité | 1,5-2,0 g/cm³ |
| Module d'élasticité | 20-35 GPa |
3. Avantages des cornières structurelles en PRF
Les cornières structurelles en PRV offrent de nombreux avantages par rapport aux matériaux traditionnels comme l'acier, l'aluminium ou le bois.
3.1. Léger et résistant
-
Jusqu'à 70% plus léger que l'acier tout en conservant une force élevée.
-
Plus facile à transporter, à manipuler et à installer.
3.2. Résistance à la corrosion et aux intempéries
-
Idéal pour environnements marins, industriels et extérieurs où l'exposition à l'humidité, au sel et aux produits chimiques est fréquente.
-
Élimine le besoin de revêtements protecteurs et entretien contre la rouille.
3.3. Non conducteur et non magnétique
-
Sans danger pour les installations électriques et Salles d'IRM dans les établissements médicaux.
-
Utilisé dans centrales électriques, sous-stations et tours de télécommunications pour prévenir les risques électriques.
3.4. Faible entretien et longue durée de vie
-
Contrairement à l'acier, le PRV n'a pas besoin de peinture, galvanisation ou revêtement pour assurer la durabilité.
-
Résistant à la dégradation biologique telle que pourriture, moisissures et dégâts d'insectes.
-
Longue durée de vie 20-50 ans en fonction de l'application et de l'environnement.
3.5. Facilité de fabrication et d'installation
-
Peut être coupé, percé et assemblé en utilisant des outils standard.
-
Aucune soudure requise, rendant l'installation plus sûre et plus facile.
-
Des formes et des tailles sur mesure peuvent être fabriquées selon les besoins.
4. Inconvénients des angles structurels en PRF
Malgré ses nombreux avantages, le cornière structurelle en PRF présente certaines limitations :
4.1. Coût initial plus élevé
-
Plus cher que les matériaux traditionnels comme l'acier ou l'aluminium, à unité égale.
-
Cependant, le coûts d'entretien réduits et longue durée de vie peut compenser l'investissement initial.
4.2. Rigidité inférieure à celle de l'acier
-
Déflexion plus élevée sous charge, nécessitant un renforcement supplémentaire dans certaines applications.
-
Pas toujours adapté à structures à haute capacité de charge sauf si elles sont correctement conçues.
4.3. Dégradation par les UV
-
exposition prolongée à lumière directe du soleil peut entraîner une dégradation de la surface et une décoloration.
-
Nécessite revêtements résistants aux UV pour une utilisation extérieure prolongée.
4.4. Performances limitées à haute température
-
Les matériaux FRP standard peuvent ramollir à des températures supérieures à 150-200°C.
-
Des résines spéciales haute température (telles que les résines phénoliques) sont nécessaires pour les environnements sujets aux incendies.
4.5. Difficile à recycler
-
Les matériaux FRP sont difficilement recyclable par rapport à l'acier ou à l'aluminium.
-
Les options d'élimination sont limitées, bien que certaines entreprises se spécialisent dans le recyclage des matériaux composites.
5. Applications des cornières structurelles en PRF
Grâce à leurs excellentes propriétés, les cornières structurelles en PRV sont largement utilisées dans diverses industries.
5.1. Applications industrielles
-
Usines de traitement chimique : Supports et structures pour équipements exposés à des produits chimiques corrosifs.
-
Traitement de l'eau et des eaux usées : Supports structuraux, passerelles et plateformes résistants à l'humidité et aux produits chimiques.
5.2. Secteur maritime et offshore
-
Construction de quais et de jetées : Résistant à l'eau salée et ne se corrode pas comme l'acier.
-
Construction navale : Utilisé dans les composants non structuraux nécessitant des matériaux légers et résistants à la corrosion.
5.3. Infrastructures et construction
-
Ponts et passerelles : Utilisé dans les passerelles piétonnes et les structures d'accès en environnements corrosifs.
-
Applications ferroviaires et routières : Structures non conductrices pour supports de signalisation ferroviaire et sous-stations électriques.
5.4. Électricité et télécommunications
-
Distribution de l'énergie : Utilisé dans les environnements à haute tension où les structures métalliques présenteraient des risques.
-
Tours de télécommunications : Supports et cadres pour structures d'antennes et panneaux de communication.
6. Conclusion
Les cornières structurelles en PRV offrent une excellente alternative à l'acier, à l'aluminium et au bois dans les applications nécessitant résistance à la corrosion, légèreté et isolation électrique. Leur longue durée de vie, faible entretien et facilité de fabrication les rendre idéaux pour applications industrielles, maritimes, d'infrastructure et électriques.
Cependant, coûts initiaux plus élevés, rigidité moindre et options de recyclage limitées Il convient d'en tenir compte lors du choix du PRV par rapport aux matériaux traditionnels. Une conception et un choix de matériaux appropriés peuvent maximiser les avantages des cornières structurelles en PRF, ce qui en fait une solution précieuse pour environnements difficiles.
Angle structurel en PRF
Série :
Principaux produits >application
Applications industrielles, maritimes et offshore, infrastructures et construction, électricité et télécommunications
Marque :
TFcomposite
Nom du produit :
Angle structurel en PRF
Matériel :
Fibre de verre
Couleur :
Gris, Autre
FAQ
Q :
Quelle est la durée de vie des pièces en PRV de forme spéciale ?
UN :
Les pièces en PRV de forme spéciale ont une durée de vie de plus de 25 ans, surpassant largement de nombreux matériaux traditionnels tels que le bois (5 à 10 ans) ou l'acier (10 à 15 ans, selon les conditions).
Q :
Les pièces en PRV de forme spéciale peuvent-elles être utilisées à l'extérieur ?
UN :
Oui ! Les pièces en PRV de forme spéciale sont extrêmement résistantes aux UV et aux intempéries, ce qui les rend idéales pour une utilisation en extérieur dans des environnements difficiles tels que les applications marines, les usines chimiques et les infrastructures.
Q :
Quelles sont les dimensions et tailles typiques des pièces de forme spéciale en PRV ?
UN :
Les dimensions des pièces en PRV de formes spéciales varient considérablement selon l'application et la conception. Cependant, les dimensions courantes sont les suivantes : Longueur : personnalisable selon les exigences du projet (généralement de 3 m à 6 m). Épaisseur : généralement de 3 mm à 50 mm, voire plus selon les besoins de résistance. Largeur : adaptable à la forme et à la fonction requises (des petits profilés aux grandes plaques). Des formes sur mesure, telles que des profilés courbes, angulaires et creux, peuvent être réalisées pour répondre précisément aux spécifications de conception.
Autres produits connexes